URL: https://www.desy.de/news/news_search/index_eng.html
Breadcrumb Navigation
DESY News: Platinum Forms Nano-Bubbles
News
News from the DESY research centre
Platinum Forms Nano-Bubbles
Platinum, a noble metal, is oxidised more quickly than expected under conditions that are technologically relevant. This has emerged from a study jointly conducted by the DESY NanoLab and the Vienna University of Technology. Devices that contain platinum, such as the catalytic converters used to reduce exhaust emissions in cars, can suffer a loss in efficacy as a result of this reaction. The team around principal author Thomas Keller, from DESY and the University of Hamburg, is presenting its findings in the journal Solid State Ionics. The result is also a topic at the users' meeting of DESY's X-ray light sources with more than 1000 participants currently taking place in Hamburg.
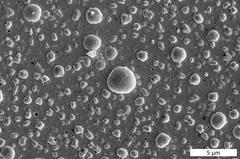
In the scanning electron microscope the platinum film shows many bubbles after the electrochemical experiment. Credit: DESY, Satishkumar Kulkarni
The scientists studied a thin layer of platinum which had been applied to an yttria-stabilised zirconia crystal (YSZ crystal), the same combination that is used in the lambda sensor of automotive exhaust emission systems. The YSZ crystal is a so-called ion conductor, meaning that it conducts electrically charged atoms (ions), in this case oxygen ions. The vapour-deposited layer of platinum serves as an electrode. The lambda sensor measures the oxygen content of the exhaust fumes in the car and converts this into an electrical signal which in turn controls the combustion process electronically to minimize toxic exhausts.
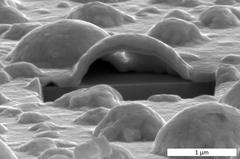
Electron microscope view into the interior of a platinum bubble. The cross-section was exposed with a focused ion beam. Below the hollow Pt bubble the angular YSZ crystal can be seen. Credit: DESY, Satishkumar Kulkarni
The scientists used a so-called focused ion beam (FIB) as a sort of ultrasharp scalpel in order to slice open the platinum bubbles and examine their inside more closely. They found that the inner surface of the bubbles was lined with a layer of platinum oxide which could be up to 85 nanometres thick, much thicker than expected.
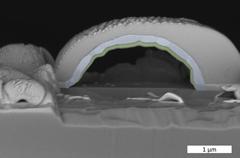
The chemical element analysis of the platinum bubble provided with a protective layer shows an outer metallic shell made of platinum (blue) and an inner shell made of platinum oxide (green). Credit: DESY, Satishkumar Kulkarni/Thomas F. Keller
Until Friday, users of the PETRA III and FLASH X-ray light sources and the European XFEL X-ray laser will meet at DESY in Hamburg. With a total of more than 1000 registrations from 30 nations, this meeting is the largest of its kind in the world. In more than 30 plenary lectures and 18 satellite workshops as well as on more than 350 scientific posters, new investigation techniques, analysis methods and results will be presented and applications and further developments of X-ray light sources will be discussed. One of the main roles this year will be the planned expansion of DESY's X-ray ring PETRA III into the ultimate 3D X-ray microscope PETRA IV, which will deliver a hundred times more detailed images from the nanocosmos. Around 80 companies will be presenting their highly specialized products for cutting-edge research at an accompanying industrial trade fair.
Reference:
Nano-scale oxide formation inside electrochemically-formed Pt blisters at a solid electrolyte interface; T.F. Keller, S. Volkov, E. Navickas, S. Kulkarni, V. Vonk, J. Fleig, A. Stierle; „Solid State Ionics“, 2019; DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2018.11.009



