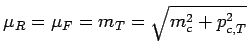 , where
, where
Recent measurements of inclusive photoproduction of ![]() mesons were
performed by H1 [7] and by ZEUS [19]
using the decay channel
mesons were
performed by H1 [7] and by ZEUS [19]
using the decay channel
![]() with
with
![]() . The
. The ![]() signal used for the ZEUS analysis
is shown in fig.11 in section 5.
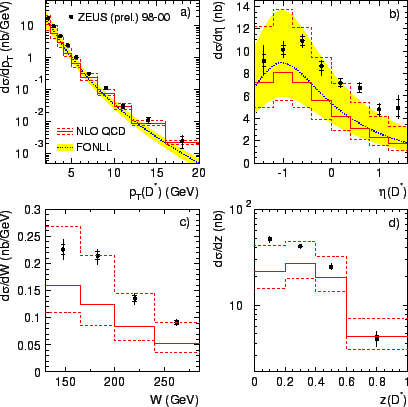
In fig.21 the ZEUS data are compared with predictions
from two next-to-leading order calculations, namely the fixed order
massive calculation FMNR [80]
and the matched calculation FONLL [92] (sections 2.1
and 3.2.1).
For the calculations the scale parameters are chosen
to be
signal used for the ZEUS analysis
is shown in fig.11 in section 5.
In fig.21 the ZEUS data are compared with predictions
from two next-to-leading order calculations, namely the fixed order
massive calculation FMNR [80]
and the matched calculation FONLL [92] (sections 2.1
and 3.2.1).
For the calculations the scale parameters are chosen
to be
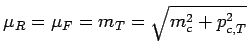 , where
, where ![]() is the renormalization scale
parameter and
is the renormalization scale
parameter and ![]() is the factorization scale parameter, and
is the factorization scale parameter, and ![]() GeV. The uncertainties
are estimated by variation of
GeV. The uncertainties
are estimated by variation of ![]() from
from ![]() to
to ![]() and
and
![]() from
from ![]() GeV to
GeV to ![]() GeV.
Good general agreement is seen with relatively large theoretical uncertainties
as estimated by simultaneous variation of the renormalization scale and
the mass of the charm quark. The central values of the NLO
predictions reproduce the shape of the d
GeV.
Good general agreement is seen with relatively large theoretical uncertainties
as estimated by simultaneous variation of the renormalization scale and
the mass of the charm quark. The central values of the NLO
predictions reproduce the shape of the d![]() distribution and general trends of the
distribution and general trends of the
![]() distributions.
However, the central NLO predictions significantly underestimate the data
over almost the whole kinematic range.
The FONLL predictions do not provide a better description of the
data than does the NLO calculation. For large
distributions.
However, the central NLO predictions significantly underestimate the data
over almost the whole kinematic range.
The FONLL predictions do not provide a better description of the
data than does the NLO calculation. For large ![]() ,
the FONLL predictions lie further below the data than does the NLO calculation.
,
the FONLL predictions lie further below the data than does the NLO calculation.
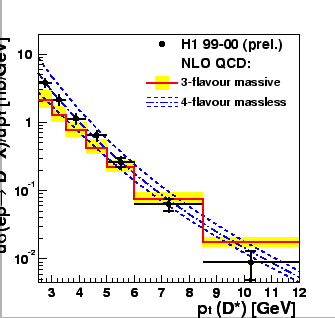
In fig.22 ![]() photoproduction data
from H1 are shown [7].
In this data sample the
low angle scattered electron is detected in an electron detector
situated 33 m away from the interaction point close to the beam pipe
in electron direction. This requirement, necessary for trigger purposes,
leads to a constraint on the range in
photoproduction data
from H1 are shown [7].
In this data sample the
low angle scattered electron is detected in an electron detector
situated 33 m away from the interaction point close to the beam pipe
in electron direction. This requirement, necessary for trigger purposes,
leads to a constraint on the range in
![]() of the data sample to
of the data sample to
![]() GeV and
restricts the statistical precision. The range in
GeV and
restricts the statistical precision. The range in ![]() is restricted to
is restricted to ![]() GeV
GeV![]() .
The data are compared with the fixed order massive
calculation from [80] and the massless calculation
from [96].
For the massive calculation the renormalization and factorization scales were
chosen as
.
The data are compared with the fixed order massive
calculation from [80] and the massless calculation
from [96].
For the massive calculation the renormalization and factorization scales were
chosen as
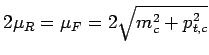 , different
from the choice of ZEUS (see above).
For calculation in the 4-flavour massless scheme
the BKK fragmentation function has been applied [96,98]
and the renormalization and factorization scales
have been chosen as
, different
from the choice of ZEUS (see above).
For calculation in the 4-flavour massless scheme
the BKK fragmentation function has been applied [96,98]
and the renormalization and factorization scales
have been chosen as
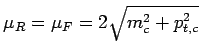 for
the central prediction.
The theories agree in general with the data. However, the massive
calculation appears to produce somewhat too hard a
for
the central prediction.
The theories agree in general with the data. However, the massive
calculation appears to produce somewhat too hard a ![]() spectrum while
the massless calculation fits the data better both in shape and in normalization.
spectrum while
the massless calculation fits the data better both in shape and in normalization.
 |
 |