CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField module
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.forcefield(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
objectTemplate for a general force field
- eAngles = 0.0
- eBonds = 0.0
- eCoul = 0.0
- eDihdedral = 0.0
- eNonbonbded = 0.0
- getBonded(molX, topol)[source]
input: molX: geometry of the molecule as flat numpy array topol: topology of the molecule
Output: energy,gradient energy: energy of bonded interaction gradient: gradient of the energy as flat numpy array
- getConstraints(geom, der=False)[source]
returns constraints
Input: geom: geometry of molecule, numpy array (natoms,3) der: (optionial) boolen Flag for wheter to provide dg as output
Output: if der, output is g,dg else, output is g
g: deviation in constraints, n-dim numpy array dg: derivative of constraints with respect to coordinates, numpy array of shape (n,na,3)
- getNonBondedInteractionPairs()[source]
returns the atom pairs that experience non-bonded interaction (LJ + coulomb) within the molecule
- getNonBondedInteractionPairsFudgeLJ()[source]
returns the fudge factor non-bonded interaction (LJ) within the molecule
- getNonBondedInteractionPairsFudgeQQ()[source]
returns the fudge factor non-bonded interaction (Coulomb) within the molecule
- getSigmaNuc(sigma_case)[source]
Returns array with the spread (sigma) of the nuclear charge for each atom in a gaussian nuclear model. Sigma is parsed to the QCE.
ho(r) = Z_i * ( rac{1}{2 pi sigma_i^2})^(2/3) * exp(-r^2 / (2 sigma_i^2))
- sigma_case: string or float, optional
If float, it is used as sigma for all atoms. If string, it can be either ‘covrad’, use the covalent radius of the atoms; or try to convert the string to a dictionary of the form {‘atom_name’: sigma_value}. Default is ‘covrad’.
sigma_nuc: (n_atoms,) ndarray of floats
- getVGeom(geom, noM=False)[source]
Input: geom: geometry as 2 dim numpy array geom[number of atoms, 3] noM: boolean, whether virtual sites for this molecule should be skipped
Output: vGeom, gM vGeom: geometry with virtual sites as 2 dim numpy array geom[number of atoms, 3] gM: Jacobi matrix elements as list ot tuples (ai,i,bj,j,g) ai: index of real atom i: index of atom coord (0…2) bj: index of virtual site j: index of virtual site coord (0…2) g: derviative dj / di
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.furfuralFF(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
forcefield
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.jointForceFields(topol, LJCombRule='OPLS', waterForcefield=None, molecule2ffstr=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
object- coulomb_egrad(dist_norm, dist_uvec, grad_shape, fudgeFactor)[source]
Calculate the Coulomb interaction energy and gradient.
- Parameters:
dist_norm ((n_nonbonded) ndarray of floats.) – Norm of the distance between all pairs of atoms.
dist_uvec ((n_nonbonded, 3)) – Unit vector between all pairs of atoms.
grad_shape (tuple of int.) – Shape of the gradient (n_nuclei, 3)
fudgeFactor ((n_nonbonded) ndarray of floats.) – Scaling factor for each non-bonded pair
- Returns:
energy_coul (float.) – Coulomb interaction energy.
gradient_coul ((n_nuclei, 3) ndarray of float.) – Gradient of the Coulomb interaction energy.
- geomWithVirtualSites(geom, listNoM=[])[source]
Function translates geometry into geometry with virtual sites that can be used for Coulomb calculation.
- Parameters:
geom ((n_atoms, 3) ndarray of floats.) – Positions of each atomic nuclei.
listNoM (list, optional) – List of atom indices for which virtual sites should be skipped, by default []
- Returns:
vGeom ((n_atoms, 3) ndarray of floats.) – Geometry with virtual sites.
vGeomD (list.) –
- List of elements of the Jacobian matrix between real and virtual geometry
- each element is a tuple (ai, i, aj, j, g), where:
ai: real geometry atomic index.
i: real geometry coordinate index 0…2.
aj: virtual geometry site index.
j: virtual geometry coordinate index 0…2.
g: derivative d r_j / d r_i.
- getEnGrad(x, listNoM=[])[source]
This subroutine calculates the energy and the gradient along all nuclear coordinates. At the moment is able to calculate the energy and the gradient of the following interactions:
Bonded interactions
Lennard-Jones interaction
Coulomb interaction (deactivated for electrostatic embedding)
- Parameters:
x ((3 * n_atoms) ndarray of float.) – Coordinates of the nuclear centers.
listNoM (list[int], optional) – Indices labeling the atoms for which virtual sites are disabled, by default []
- Returns:
energy (float.) – Energy given by the force field. Units are Hartree!
gradient ((3 * n_atoms) ndarray of float.) – Gradient of the energy along all nuclear coordinates as flat numpy array. The order is as in the input. Units are Hartree/Bohr.
- getRattleCorrection(vec0, vec1, dt, case='pos')[source]
This method returns the correction to the position and velocity of a constrained geometry needed for the RATTLE algorithm. If case = “pos”, vec0 and vec1 represent r(t) and r(t+dt) without constraints, respectively. In this case, the correction to v(t+dt/2) is returned as it is needed to calculate r(t+dt) with constraints. If case = “vel” vec0 and vec1 represent r(t+dt) with constraints and v(t+dt) without constraints. In this case the correction to v(t+dt) with constraints is returned directly.
- Parameters:
vec0 ((3 * n_atoms) ndarray of float.) – r(t) [“pos”] or r(t+dt) [“vel”] without constraints applied.
vec1 ((3 * n_atoms) ndarray of float.) – r(t+dt) [“pos”] or v(t+dt) [“vel”] with and without constraints applied, respectively.
dt (float) – Timestep
case (str, optional) – Flag to calculate correction to position [“pos”] or velocity [“vel”], by default “pos”
- Returns:
correction – Correction to v(t+dt/2) [“pos”] or v(t+dt) [“vel”] for geometries with constraints.
- Return type:
(n_atoms, 3) ndarray of float.
- gradient_virt2orig(gradient, vGeomD)[source]
This function translates gradient of virtual sites into gradient of original geometry.
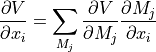
- Parameters:
gradient ((n_atoms, 3) ndarray of floats.) – Gradient at each virtual site position (some virtual positions are already real ones).
vGeomD (list) –
List of elements of the Jacobian matrix between real and virtual geometry each element is a tuple (ai, i, aj, j, g), where:
ai: real geometry atomic index.
i: real geometry coordinate index 0…2.
aj: virtual geometry site index.
j: virtual geometry coordinate index 0…2.
g: derivative d r_j / d r_i.
- Returns:
grad_res – Gradient at each atom real position.
- Return type:
(n_atoms, 3) ndarray of floats.
- lennard_jones_egrad(dist_norm, dist_uvec, grad_shape, fudgeFactor)[source]
Calculates the energy and gradient of the Lennard-Jones interaction.
- Parameters:
dist_norm ((n_nonbonded) ndarray of floats.) – Norm of the distance between all pairs of atoms.
dist_uvec ((n_nonbonded, 3)) – Unit vector between all pairs of atoms.
grad_shape (tuple of int.) – Shape of the gradient (n_nuclei, 3)
fudgeFactor ((n_nonbonded) ndarray of floats.) – Scaling factor for each non-bonded pair
- Returns:
energy_LJ (float.) – Lennard-Jones interaction energy.
gradient_LJ ((n_nuclei, 3) ndarray of float.) – Gradient of the Lennard-Jones interaction energy.
- molecule2FF = {'SOL': <class 'CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.waterFF_TIP4P2005f'>, 'UREA': <class 'CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.ureaFF'>}
- velWithVirtualSites(velocity, vGeomD)[source]
This function translates velocities of original coordinates to velocities of virtual sites.
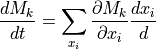
- Parameters:
velocity ((n_atoms, 3) ndarray of floats.) – Valocity of each virtual site position (some virtual positions are already real ones).
vGeomD (list) –
List of elements of the Jacobian matrix between real and virtual geometry each element is a tuple (ai, i, aj, j, g), where:
ai: real geometry atomic index.
i: real geometry coordinate index 0…2.
aj: virtual geometry site index.
j: virtual geometry coordinate index 0…2.
g: derivative d r_j / d r_i.
- Returns:
vel_res – Velocity of virtual sites.
- Return type:
(n_atoms, 3) ndarray of floats.
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.ureaFF(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
forcefield
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.waterFF_SPC(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
forcefield
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.waterFF_SPCE(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
forcefield
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.waterFF_TIP4P(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
forcefield- getVGeom(geom, noM=False)[source]
Input: geom: geometry as 2 dim numpy array geom[number of atoms, 3] noM: boolean, whether virtual sites for this molecule should be skipped
Output: vGeom, gM vGeom: geometry with virtual sites as 2 dim numpy array geom[number of atoms, 3] gM: Jacobi matrix elements as list ot tuples (ai,i,bj,j,g) ai: index of real atom i: index of atom coord (0…2) bj: index of virtual site j: index of virtual site coord (0…2) g: derviative dj / di
For the TIP4P water molecule, the oxygen geometry is swapped with the geometry of the virtual site. Hydrogen positions in vGeom are identical to geom
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.waterFF_TIP4P2005(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
waterFF_TIP4P
- class CDTK.Interfaces.ForceField.waterFF_TIP4P2005f(topol=None, **opts)[source]
Bases:
waterFF_TIP4P